Littles Law
Little's Law is a fundamental concept in the field of operations research and queueing theory, providing a simple yet powerful relationship between the average arrival rate, average queue length, and average processing time in a system. This law, named after John Little, a renowned American operations researcher, has significant implications across various industries, particularly in optimizing system performance and managing queues.
Understanding Little’s Law

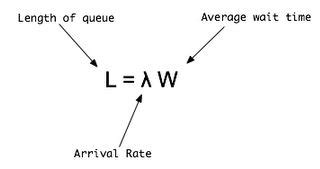
Little’s Law, often expressed as Λ = λW, is a mathematical equation that connects the average number of customers or jobs Λ in a system, the average arrival rate λ, and the average time W that a customer or job spends in the system, including waiting time and service time. In simpler terms, it states that the average number of customers in a system is equal to the average arrival rate multiplied by the average time spent in the system.
This law is a cornerstone in queueing theory, offering a straightforward yet robust tool for analyzing and optimizing systems with queues. It applies to a wide range of scenarios, from call centers and manufacturing lines to retail shops and traffic systems. By understanding and applying Little's Law, businesses and organizations can make informed decisions to improve efficiency, reduce wait times, and enhance overall customer experience.
Applications and Implications

Little’s Law has extensive applications in real-world scenarios. For instance, in a call center setting, it can be used to determine the optimal number of agents required to handle incoming calls, ensuring that wait times are minimized while maintaining high service quality. Similarly, in a hospital’s emergency department, Little’s Law can guide staffing decisions and help manage patient flow, reducing wait times and improving patient satisfaction.
In manufacturing, Little's Law can be instrumental in optimizing production lines, helping to balance the workload and ensure efficient use of resources. It can also be applied in logistics and supply chain management to streamline operations, reduce inventory levels, and improve delivery times.
Furthermore, Little's Law is not limited to physical queues. It can be applied to virtual queues in software systems, such as web servers or cloud computing platforms, to optimize resource allocation and enhance system performance. By utilizing Little's Law, organizations can make data-driven decisions to improve their operations, gain a competitive edge, and deliver superior services to their customers.
Illustrating Little’s Law with an Example
Consider a scenario in a popular coffee shop where customers typically spend an average of 5 minutes in line (including waiting and service time). If we observe that on average, 10 customers arrive every hour, we can apply Little’s Law to determine the average number of customers in the queue at any given time.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Average arrival rate (λ) | 10 customers per hour |
| Average time in the system (W) | 5 minutes (or 1/12 hour) |
| Average number of customers in the system (Λ) | Little's Law: Λ = λW |
| Λ = (10 customers/hour) * (1/12 hour) | |
| Λ = 0.83 customers |

So, on average, there will be approximately 0.83 customers in the queue at any given time, which is a relatively small number, indicating an efficient system.
Benefits and Limitations of Little’s Law
Little’s Law offers several advantages. It provides a simple and intuitive understanding of queueing systems, allowing for quick assessments and optimizations. It also serves as a foundation for more complex queueing models, helping to validate their assumptions and results. Additionally, Little’s Law can be applied across various industries and scenarios, making it a versatile tool for operational research.
However, it's important to note that Little's Law assumes a steady-state system, which may not always be the case in real-world scenarios. It also relies on the average arrival rate and average time in the system, which may not always be easily measurable or constant. Therefore, while Little's Law is a powerful tool, it should be used in conjunction with other analytical techniques and real-world observations to gain a comprehensive understanding of queueing systems.
Advanced Applications and Extensions

Little’s Law can be extended and applied in more complex scenarios. For instance, it can be used in conjunction with Markov chains to model more intricate queueing systems with multiple servers or priority classes. It can also be integrated with simulation models to validate assumptions and predict system behavior under different scenarios.
Furthermore, Little's Law has been applied in the field of healthcare to optimize patient flow and reduce wait times, particularly in emergency departments and outpatient clinics. In these settings, Little's Law helps guide staffing decisions, manage resource allocation, and improve patient satisfaction.
In the realm of computer science, Little's Law is used in network modeling and analysis to optimize data flow and enhance system performance. It is also applied in cloud computing to manage virtual queues and optimize resource allocation, ensuring efficient and responsive services.
Future Implications and Conclusion
As businesses and organizations continue to seek ways to improve efficiency and enhance customer experience, Little’s Law will likely remain a vital tool in their arsenal. With the increasing use of data analytics and simulation techniques, Little’s Law can be combined with these approaches to provide even more accurate and insightful results.
Moreover, as industries become more interconnected and complex, Little's Law can be applied at the intersection of various sectors, such as healthcare and technology, to solve real-world problems and drive innovation. Its applications are not limited to queueing systems alone; Little's Law can also inform decision-making in areas such as resource allocation, inventory management, and process optimization.
In conclusion, Little's Law is a powerful and versatile concept that provides a simple yet effective understanding of queueing systems. Its applications and implications are far-reaching, offering valuable insights and guiding decisions in various industries. By harnessing the power of Little's Law, organizations can optimize their operations, improve customer satisfaction, and stay ahead in today's competitive landscape.
How accurate is Little’s Law in real-world scenarios?
+Little’s Law provides a solid foundation for understanding queueing systems, but its accuracy can be influenced by the stability and characteristics of the system. In real-world scenarios, it’s essential to validate the assumptions and consider other factors that may impact the system’s behavior.
Can Little’s Law be applied to systems with varying arrival rates and service times?
+Yes, Little’s Law can be applied to systems with varying arrival rates and service times, as long as the system is in a steady state and the average arrival rate and average time in the system can be determined.
How can Little’s Law be used in healthcare settings?
+In healthcare, Little’s Law can be applied to optimize patient flow, guide staffing decisions, and manage resources in emergency departments, outpatient clinics, and other healthcare facilities. It helps improve patient satisfaction and efficiency.



