Pressure Unit Conversion
Welcome to an in-depth exploration of the fascinating world of pressure unit conversion. As a technical expert in the field, I will guide you through the intricacies of pressure measurement and provide valuable insights into the various units of pressure, their conversions, and their practical applications.
The Importance of Pressure Unit Conversion
Pressure is an essential parameter in numerous scientific, engineering, and everyday applications. From meteorology and aviation to industrial processes and medical diagnostics, accurate pressure measurement and conversion are vital for ensuring precision, safety, and efficiency.
Pressure unit conversion allows professionals and enthusiasts alike to understand and communicate pressure values across different systems and industries. It bridges the gap between various measurement units, ensuring seamless data interpretation and comparison.
Understanding Pressure and Its Units
Pressure is a fundamental physical quantity that represents the force exerted per unit area. It is typically measured in a variety of units, each with its own unique characteristics and applications.
Common Pressure Units
Here’s an overview of some of the most commonly used pressure units:
- Pascal (Pa): The International System of Units (SI) unit of pressure. 1 Pa is equivalent to 1 N/m².
- Bar (bar): Commonly used in meteorology and industrial applications. 1 bar is approximately equal to the atmospheric pressure at sea level.
- Atmosphere (atm): Another common unit, equal to the pressure exerted by the weight of the Earth’s atmosphere at sea level.
- Pound per Square Inch (psi): Widely used in the United States and other countries for various applications, including automotive and industrial systems.
- Millibar (mbar): A metric unit often used in meteorology to measure atmospheric pressure.
- Torr (Torr): Based on the pressure exerted by a column of mercury, it is commonly used in vacuum systems and scientific research.
- Kilopascal (kPa): A practical unit for everyday pressure measurements, often used in HVAC systems and weather reporting.
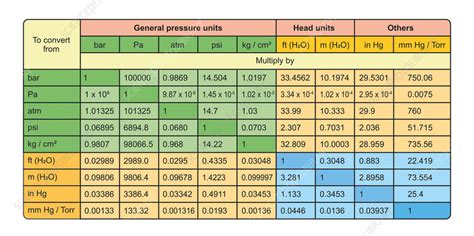
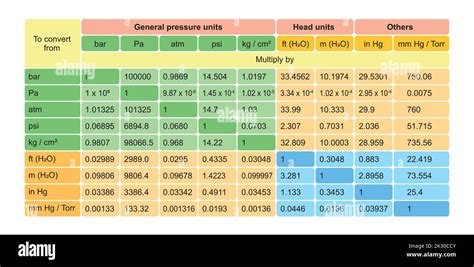
Conversion Factors and Formulas
Converting between these pressure units requires understanding the conversion factors and applying the appropriate formulas. Here are some essential conversions:
| Unit | Conversion Factor | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Pascal (Pa) | 1 Pa = 1 N/m² | Pa = N/m² |
| Bar (bar) | 1 bar ≈ 100,000 Pa | bar = Pa / 100,000 |
| Atmosphere (atm) | 1 atm ≈ 101,325 Pa | atm = Pa / 101,325 |
| Pound per Square Inch (psi) | 1 psi ≈ 6,894.76 Pa | psi = Pa / 6,894.76 |
| Millibar (mbar) | 1 mbar ≈ 100 Pa | mbar = Pa / 100 |
| Torr (Torr) | 1 Torr ≈ 133.322 Pa | Torr = Pa / 133.322 |
| Kilopascal (kPa) | 1 kPa = 1,000 Pa | kPa = Pa / 1,000 |
Practical Applications of Pressure Unit Conversion
Pressure unit conversion finds applications in a wide range of fields, each with its own unique requirements and challenges.
Meteorology and Weather Forecasting
Meteorologists rely on pressure measurements to understand atmospheric conditions and predict weather patterns. Converting between units like millibars and atmospheres is essential for interpreting and communicating weather data effectively.
Aviation and Aerospace
In aviation, pressure unit conversion is crucial for altitude calculations, engine performance, and flight planning. Pilots and engineers need to understand and convert pressure values between units like inches of mercury (inHg) and hectopascals (hPa) to ensure safe and efficient flight operations.
Industrial Processes
Industrial processes, such as manufacturing, chemical engineering, and oil and gas extraction, often involve precise pressure control. Converting between units like psi and bar is vital for maintaining optimal conditions and ensuring the safety of personnel and equipment.
Medical Diagnostics
Medical professionals use pressure measurements for various diagnostic purposes, including blood pressure monitoring and respiratory assessments. Converting between units like mmHg (millimeters of mercury) and kPa is essential for accurate patient evaluation and treatment.
HVAC Systems
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems rely on pressure measurements to maintain comfortable indoor environments. Converting between units like Pa and inHg is necessary for system design, troubleshooting, and energy efficiency calculations.
The Future of Pressure Measurement
As technology advances, the field of pressure measurement and conversion continues to evolve. Here are some insights into the future of pressure unit conversion:
Standardization and Precision
Efforts are underway to further standardize pressure units and improve their precision. This includes ongoing research and development of new pressure sensors and measurement techniques, aiming to reduce errors and enhance accuracy.
Digital Transformation
The digital age has brought about significant advancements in pressure measurement technology. Digital pressure sensors and transducers offer improved accuracy, real-time data acquisition, and remote monitoring capabilities. These innovations are revolutionizing pressure measurement across industries.
Emerging Applications
Pressure unit conversion finds new applications in emerging fields such as aerospace engineering, renewable energy, and environmental monitoring. As these industries grow, the demand for accurate pressure measurements and conversions will continue to rise.
Smart Pressure Sensors
The development of smart pressure sensors with built-in conversion capabilities is on the horizon. These sensors could potentially provide real-time, unit-independent pressure data, simplifying data interpretation and reducing the need for manual conversions.
Conclusion

Pressure unit conversion is an essential skill for professionals and enthusiasts across a wide range of industries. Understanding the various pressure units, their conversions, and their practical applications is vital for accurate data interpretation and decision-making.
As technology advances, pressure measurement and conversion will continue to evolve, driving innovation and enhancing efficiency in numerous fields. By staying informed about the latest advancements and best practices, we can ensure that pressure unit conversion remains a valuable tool for precise and effective communication of pressure data.
What is the most commonly used pressure unit in everyday life?
+The most commonly used pressure unit in everyday life is the Pascal (Pa), as it is the SI unit of pressure and is widely used in various scientific and engineering applications.
How do I convert pressure values between different units?
+To convert pressure values between different units, you need to apply the appropriate conversion factors and formulas. For example, to convert from Pascals (Pa) to Bars (bar), you would use the formula: bar = Pa / 100,000. It’s important to note the precision and accuracy required for your specific application.
Are there any online tools or calculators for pressure unit conversion?
+Yes, there are numerous online tools and calculators available that can assist with pressure unit conversion. These tools provide quick and convenient conversions between various pressure units. However, it’s always a good practice to cross-reference the results with reliable sources to ensure accuracy.